Intermittent fasting and its impact on health
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Content Courtesy : twitter.com/hyderabaddoctor/status/15887561..
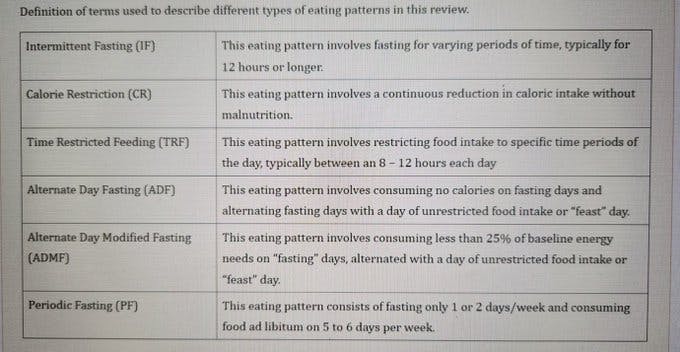
A. What is intermittent fasting (IF)? A variety of eating patterns in which no or few calories are consumed for prolonged time periods that can range from 12 hours to several days, on a recurring basis.
B. What are the different ways of Intermittent Fasting?
- Alternate-day fasting,
- 5:2 or 6:1 intermittent fasting (fasting 2 days or 1 day each week),
- Daily time-restricted feeding (Eating within 8-12 hour window and fasting during the rest of the day)
C. Definition of various types of intermittent fasting
D. Benefits of intermittent fasting
- Reduces the risk of #diabetes, lowers fasting blood glucose in diabetics
- Reduces total and LDL #cholesterol and triglycerides,
- Lowers systolic #BP
- Reduces #body #weight
- Improves focus, attention, concentration and #memory
- Reduces the rate of cognitive impairment and reduces the risk of #Alzheimers disease,
- Reduces the risk of #stroke,
- Increases the lifespan (effect on longevity seen with>5 yrs of IF)
E. Cellular, molecular & physiological responses to intermittent fasting During fasting, cells undergo adaptive stress resulting in range of effects, including increased production of antioxidants, DNA repair, autophagy (removal of damaged or dead cells)& decreased inflammation
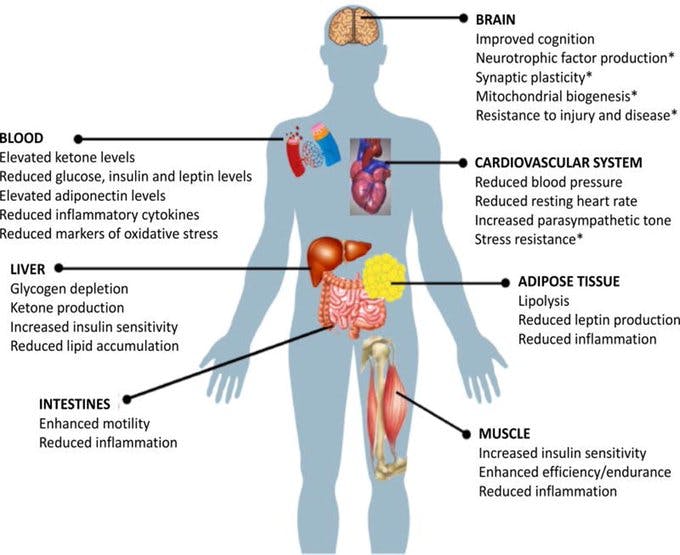
F. Mechanisms involved in IF
- Metabolic switch: Body’s preferential shift from utilization of glucose from glycogenolysis to fatty acids and fatty acid-derived ketones. Ketones are the preferred fuel for both the brain and body during periods of fasting and extended exercise.
Of relevance to weight management, this switch represents a shift from lipid synthesis and fat storage to mobilization of fat in the form of free fatty acids (FFAs) and fatty-acid derived ketones.
G. Who should not attempt intermittent fasting? Those who are
- underweight,
- under 18 years old,
- pregnant or breastfeeding women,
- having a history or currently struggling with eating disorders
H. Conclusions
- Intermittent fasting (IF) is safe for most,
- IF has beneficial effects against obesity, diabetes, high BP & cholesterol,
- IF reduces the risk of dementia and stroke,
- IF increases longevity
- IF regimen needs to be modified as per individual goals and needs.